Time : November 2, 2023
Abstract: In order to improve the operational performance of rotor spinning bearings, the application of engineering ceramics on rotor spinning bearings was studied. Analyzed the problems of steel bearings in rotor spinning, proposed the requirements and preparation process for ceramic bearing materials, and trial-produced ceramic ball hybrid bearings. They were compared with steel bearings in operation on F1603 rotor spinning machine. The results show that the service life of ceramic ball hybrid bearings is increased by 5 times compared to traditional steel bearings, the temperature rise of bearings is reduced by 30%, and the noise is reduced by 2 dB.
Keywords: rotor spinning; Ceramic ball bearings; Silicon nitride; Elastic modulus; Speed; Temperature rise; Wear resistance
The rotor spinning bearing is a special type of bearing with few parts and simple structure, but high speed, high accuracy, and reliable system performance. The yarn quality and economic benefits of rotor spinning mainly depend on the quality of the rolling bearing unit inside the rotor spinning device. It requires the rolling bearing unit to have high accuracy, high speed, reliable performance, low noise, low friction, long service life, low temperature rise, low resistance, and low maintenance. At present, domestic rotor spinning bearings are usually made of bearing steel. Due to the inherent characteristics of steel bearings, the rotor has disadvantages such as low speed, temperature rise, large vibration, high noise, and poor accuracy retention, which affects the yarn quality and production efficiency of rotor spinning. Ceramic materials have advantages such as low density, high hardness, high temperature resistance, and corrosion resistance, as well as excellent properties such as high strength and toughness. Therefore, they have broad application prospects in industries such as textiles. At present, hybrid ceramic bearings (steel rings and ceramic rolling elements) have been widely used in machine tool spindle bearings and other high-speed or precision equipment. Due to its excellent performance and broad development prospects, ceramic bearings have become a hot topic in the development and application of high-tech in the world, and have become one of the symbols of the material technology revolution in the mechanical industry.
The ceramic material used for manufacturing rolling bearing parts should have the following characteristics:
According to the working conditions, the HQF2256/01A bearing used in the F1603 rotor spinning machine was selected as the experimental research object. The main parameters of the bearing are as follows: the specification is D22 mm × D10 mm × 56 mm, with a speed of 30 000 r/m in to 60 000 r/m in, lubricated with grease. Considering the structural characteristics of the bearing, a hybrid ceramic bearing is adopted, which is assembled using the outer ring and core shaft made of bearing steel and the rolling element made of Si3N4 ceramic.
3.1 Manufacturing process
Raw material preparation – mixing – forming – sintering – rough machining – precision machining – assembly – finished product inspection
3.2 Manufacturing of blanks
The process is as follows: firstly, in the raw material preparation process, the required Si3N4 ceramic powder is mixed with Y2O3 2A l2O3 and MgO sintering aids in a ratio of 100:10 to prepare the raw material powder; Secondly, the powder is loaded into the mold according to the required amount and formed using isostatic pressing method; Finally, the formed green ball is loaded into a graphite sagger and subjected to hot isostatic pressing sintering at a temperature of (1880 ± 10) ℃ to achieve complete densification.
There are many factors that affect the performance of silicon nitride materials, among which material porosity and large particle inclusions can seriously shorten the rolling contact life of silicon nitride. The size of material porosity depends on sintering method, additives, powder particle size, and purity. The particle size of the material powder in this experiment is controlled at 1 μ Below m and using chemical preparation methods to improve its purity.
The use of Y2O3 2A l2O3 composite additives can achieve optimal sintering of silicon nitride. Because this additive can ensure the formation of Y2Si2 A l2O2N liquid phase, silicon nitride is sintered most fully in this phase. By introducing Y2O3 2A l2O3 additive, high-strength silicon nitride ceramics can be prepared.
Introducing MgO as an additive can ensure the formation of liquid phase and produce high-density hot-pressed silicon nitride materials. The formation of the liquid phase is the result of the interaction between magnesium oxide and silicon dioxide (always involved in the formation of Si3N4 particle surface films).
3.3 Processing and Assembly of Ceramic Balls
The processing process of ceramic balls is similar to that of steel balls, requiring multiple processes of initial and fine grinding. The processing of ceramic balls mainly uses diamond abrasives and grinding tools. Fundamentally speaking, the main factors that affect the grinding process are abrasives and abrasive liquid films. For ceramic ball bearings used at high speeds, according to the requirements of rolling bearings, the machining accuracy of ceramic balls should generally be above G10 level, and this test requires an accuracy of G5 level.
The assembly process of ceramic bearings is the same as that of steel bearings, both of which need to go through processes such as sorting, fitting, ball adding, riveting, cleaning, and inspection. The difference is that the assembly of ceramic bearings should pay more attention to bumps and bruises, especially in the ball adding process, special ball adding machines must be used to add balls to avoid micro cracks in the ceramic balls caused by bumps and bruises.
4.1 Temperature rise and working life
A temperature rise test was conducted on the F1603 rotor spinning machine using a ceramic ball mixed bearing and a steel bearing, and the results are shown in Figure 1. The experiment shows that the higher the speed, the greater the difference in temperature rise between the two. This is because the volume mass of the steel ball is 215 times that of the ceramic ball, so as the spindle speed increases, the centrifugal force of the steel ball will also sharply increase, causing greater contact stress in the bearing, leading to increased friction and higher temperature rise in the bearing. At the same time, the elastic modulus and hardness of silicon nitride ceramics are 115 and 213 times that of bearing steel, while the thermal expansion coefficient is only 30% of that of bearing steel. This not only improves the stiffness and lifespan of bearings, but also makes the fit clearance of bearings change less under different temperature rise conditions, making them reliable in operation. In addition, ceramics are resistant to high temperatures and do not stick to metals. Obviously, using silicon nitride ceramics to make spheres is more suitable for high-speed rotation.
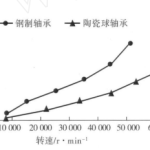
Figure 1 Comparison of temperature rise between two types of bearings
In addition, according to the calculation formula of bearing friction torque (M= μ Pd/2, where M is the friction torque, μ It can be seen that after sintering, ceramics have a smaller friction coefficient than bearing steel, resulting in a smaller bearing friction torque and therefore a smaller friction force. A comparative test was conducted on the service life of ceramic ball hybrid bearings and steel bearings on F1603 rotor spinning machine under the following conditions: speed of 50000 r/m in, and rotor diameter of 57 mm. The results show that the service life of the ceramic ball hybrid bearing rotor is 5 times that of steel bearings, and it has good accuracy retention. It not only effectively avoids bamboo yarn caused by unstable rotor operation, but also reduces maintenance times.
4.2 Rigidity
Measure the axial static stiffness of ceramic ball hybrid bearings and steel bearings on an XRY stiffness measuring instrument. The experimental results are shown in Figure 2. The results indicate that the rigidity of ceramic ball hybrid bearings increases due to the fact that the elastic modulus of ceramics is much higher than that of bearing steel.
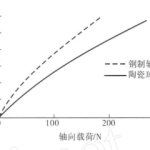
Figure 2 Comparison of axial stiffness between two types of bearings
4.3 Wear resistance and reliability
Due to the inherent wear reduction, anti wear, and lubrication functions of ceramic materials, the working reliability and service life of the rotor can be greatly improved under boundary lubrication conditions. The results show that the noise of the rotor can be reduced by more than 2 dB.
Engineering ceramic bearings are used for rotor spinning. Compared with ordinary steel bearings, they have good comprehensive performance, low temperature rise, high rigidity, good wear resistance and reliability, long service life, and can adapt to high-speed and high-temperature working environments. Due to its good accuracy retention, it can significantly improve the yarn quality and improve the production efficiency of rotor spinning. However, due to the processing characteristics of ceramics, the processing process is complex, the processing efficiency is low, and the processing cost is high. At present, the research on the processing technology of large-scale ceramic bearings in China is still in its initial stage. With the continuous development of ceramic processing technology, ceramic bearings will be increasingly widely used in fields such as textiles.
2023 New Week XZBRG Product Recommendation:
Vollkeramik-Kugellager, die vollständig aus Keramikmaterial bestehen. Innere/äußere Laufringe und Kugeln bestehen entweder aus Siliziumnitrid (Si3N4), Zirkoniumoxid (ZrO2) oder Siliziumkarbid (SiC). Sie sind vollrollig (ohne Käfig) oder mit einem Käfig aus PEEK oder PTFE erhältlich. Vollkeramiklager sind für Anwendungen mit mittlerer Belastung und mittlerer Geschwindigkeit. Es ist nicht möglich, die Rundheit des Innen- und Außenrings zu erreichen, die bei Präzisionsstahllagern zu finden ist, daher haben Vollkeramiklager niedrigere Drehzahlwerte.

