Time : November 22, 2023
Abstract: The characteristics of TiCN material are analyzed. 160 # / 180 # alumna grinding wheel with ceramic agglutinative agent is preliminarily selected for the process of raceway of bearing rings ,120 # / 160 # and 160 # / 180 # wheel for rough grinding and fine grinding of side faces and inner diameter and outer diameter of rings respectively. The Machining technology is working – out for rings made of ceramic – metal.
Key words: TiCN ceramic – metal ;rolling bearing ;ring ;grinding ;technology
One of the main methods for processing engineering ceramic materials is grinding. Due to the high hardness of engineering ceramic materials, micro cracks and other defects are prone to occur during the processing process. At the same time, grinding wheels are expensive, grinding efficiency is low, and processing costs are high (general processing costs account for 65% to 90% of the total cost). Therefore, it is very important to develop appropriate processing techniques to process ceramic parts as high-quality, efficient, and low-cost as possible.
The characteristics of grinding process for structural ceramic materials: ① The grinding force ratio is large (about 3-14), which is much higher than that of ordinary grinding wheel processing steel (about 1.6-1.9), with high grinding resistance and low processing efficiency. ② The hardness of the material is high, and the grinding ratio is much smaller than that of steel. At the same time, the cost of abrasive tools is high, resulting in high processing costs.
The grinding process and surface quality of structural ceramic materials are different from those of metal materials and ordinary brittle materials. The high hardness, high strength, and certain brittleness of structural ceramic materials determine that their grinding process is mainly characterized by brittle fracture, accompanied by elastic scratches, plastic flow deformation, and other phenomena, making the grinding surface quality difficult to control.
Diamond grinding wheels are commonly used for grinding structural ceramics. With the improvement of material properties, the research on new grinding methods for structural ceramics has also attracted increasing attention from researchers. Currently, new methods that can be used for structural ceramic grinding include constant pressure grinding, ELID mirror surface grinding, and so on.
TiCN ceramics are Ti (C, N) based ceramics. Compared to metals, they are similar to commonly used structural ceramics and have properties comparable to hard alloys. They have characteristics such as high temperature resistance, high hardness, corrosion resistance, and low coefficient of expansion.
2.1 Selection of grinding wheels
Due to the advantages of high bonding strength, high stiffness, good heat resistance and wear resistance, and no fear of moisture, ceramic bonded alumina grinding wheels are selected to process the inner and outer ring grooves of TiCN metal ceramic bearings. As metal bonded diamond grinding wheels are commonly used for rough and fine grinding of hard alloys and ceramics, metal bonded diamond grinding wheels are used for the end face and inner and outer diameters of TiCN metal ceramic rings. The particle size of the grinding wheel has a significant impact on the surface quality and grinding efficiency of the machining process. In the preliminary test, the blockage is very serious when grinding TiCN cermets with a diamond grinding wheel with a particle size of 230 #/270 #. Therefore, the diamond particle size of the inner and outer diameters and end faces of the rough grinding ring is 120 #/140 #, and the particle size of the precision grinding wheel is 160 #/180 #; The particle size of the inner and outer groove grinding wheel is 160 #/180 #.
2.2 Grinding process of TiCN metal ceramic bearing ring
Taking 6205 bearing as an example, the main machining surfaces of its inner and outer rings include two end faces, inner and outer diameters, and inner and outer ring grooves. Among all machining surfaces, the requirements for the inner and outer ring grooves are the highest, and the machining quality of the grooves directly affects the operational performance of the bearing.
Due to the non magnetic nature of TiCN cermet ferrules, specialized pneumatic fixtures must be designed for the machining of ferrule channels. The fixture structure is complex and requires high accuracy. During the trial production of TiCN cermet ferrules, the structure shown in Figure 1 is used. A thin bearing steel ring is bonded to one end face of the TiCN cermet ferrule to facilitate magnetic adsorption and clamping on a channel grinder, achieving channel processing.

Figure 1 Schematic diagram of ceramic to steel bonding
Outer ring processing process (Figure 2): Grind one end face of the steel ring as the reference for subsequent processing → Positioning and machining ceramic end faces with steel end faces → Positioning the outer circle with the steel end face, clamping and processing the inner diameter to the size → Steel end face and inner circle positioning processing outer diameter to size → Steel end face and outer diameter positioning, magnetic adsorption processing of outer ring grooves → Debonding → Grind off the adhesive ceramic end face to size.

Figure 2 Dimensions of TiCN cermet outer ring
Inner ring processing process (Figure 3): Grinding one end face of the steel ring as the reference for subsequent processing → Positioning and machining ceramic end faces with steel end faces → Positioning the outer circle with the steel end face and clamping the rough grinding inner diameter → Steel end face and inner circle positioning precision grinding outer diameter to size → Steel end face and outer diameter positioning, magnetic adsorption processing of inner ring grooves → Debonding → Grind off the adhesive ceramic end face to size.
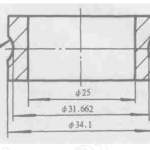
Figure 3 TiCN Cermet Inner Ring Dimensions
The grinding of the inner and outer raceways of TiCN cermet is carried out using ordinary alumina grinding wheels, with the following grinding parameters:
Grinding parameters for outer ring channel: grinding wheel speed 18 m/s, workpiece speed 120 r/min, radial feed rate rough grinding 0 05 mm/min, precision grinding 0 005 mm/min.
Inner ring groove grinding parameters: grinding wheel speed 25 m/s, workpiece speed 120 r/min, radial feed rate coarse grinding 0 05 mm/min, precision grinding 0 008 mm/min.
The grinding parameters for grinding the end face and inner and outer diameters of the ring with a diamond grinding wheel are as follows.
Face grinding parameters: grinding wheel speed 25 m/s, workpiece speed 12 mm/min, vertical feed semi precision grinding 0 015 mm, precision grinding 0 01 mm, cross feed semi precision grinding 2 mm/s, precision grinding 1 mm/s. Outer diameter grinding parameters: grinding wheel speed 25 m/s, workpiece speed 12 m/s, radial feed semi precision grinding 0 015 mm/min, precision grinding 0 005 mm/min, longitudinal feed semi precision grinding 1 m/s, precision grinding 0 5 m/s.
Inner diameter grinding parameters: grinding wheel speed 20 m/s, workpiece speed 16 mm/min, radial feed semi precision grinding 0 01 mm/min, precision grinding 0 005 mm/min, longitudinal feed semi precision grinding 2 mm/s, precision grinding 1 mm/s.
We have selected a grinding wheel for processing TiCN cermet ferrules, developed a grinding process for TiCN cermet ferrules, and produced TiCN cermet ferrules. If mass production is to be carried out, further improvement of the ring processing technology is needed to adapt to the mass production of rings.
Xinzhou Bearing provide a wide range of ceramic ball options across a variety of sizes. Material options include Silicon nitride (Si3N4), Zirconia (ZRO2), Alumina (Al2O3) and Silicon carbide (SIC) from 0.4mm to just over 115mm in diameter with the most common sizes in between. Precision grades provided are 5, 10, 16, 25 and 100.
https://www.xzballbearing.com/product-cat/ceramic-balls/
